Introduction
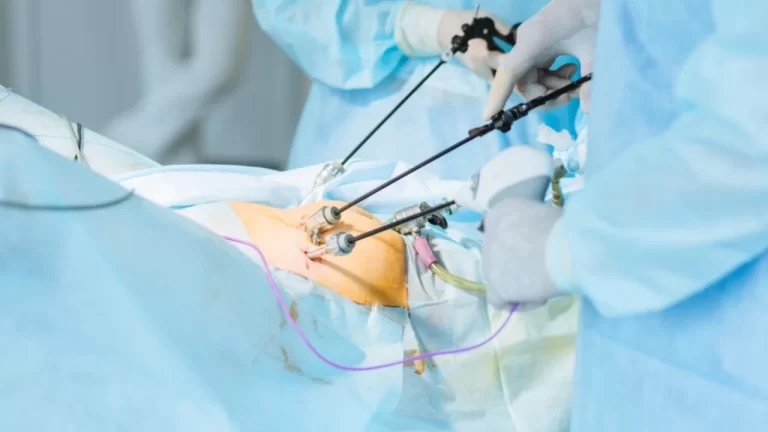
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS), is a modern surgical technique that has transformed the field of surgery. Unlike traditional open surgery, laparoscopy involves small incisions, specialized instruments, and a camera to perform various procedures with precision and minimal trauma to the patient. This method is widely used for abdominal and pelvic surgeries, including gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and appendix removal.
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is a procedure where surgeons use a small camera, called a laparoscope, and thin surgical instruments to operate through tiny incisions. The laparoscope transmits high-definition images to a monitor, allowing surgeons to see and navigate inside the body with greater accuracy.
How is Laparoscopic Surgery Performed?
- Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- Small Incisions: Surgeons make 3 to 5 small incisions (typically 0.5 to 1 cm) in the abdomen.
- Insertion of the Laparoscope: A thin tube with a camera and light is inserted through one of the incisions.
- Gas Inflation: The abdominal cavity is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create space for better visibility.
- Surgical Procedure: Specialized instruments are used through the other incisions to perform the surgery.
- Closure: After completing the procedure, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with stitches or surgical glue.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
 Minimally Invasive
Minimally Invasive
– Small incisions mean less pain and quicker healing. Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) refers to surgical techniques that use small incisions, specialized instruments, and advanced technology to perform complex procedures with less pain, minimal scarring, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery. This approach has transformed surgical care, offering patients a safer and more effective alternative.


 Reduced Blood Loss
Reduced Blood Loss
– Minimally invasive surgery involves smaller incisions and precision techniques, leading to significantly less blood loss compared to traditional open surgery. This reduces the need for blood transfusions, lowers the risk of complications, and promotes a faster recovery for patients.
 Faster Recovery
Faster Recovery
– Minimally invasive procedures cause less trauma to the body, leading to reduced pain, minimal scarring, and shorter hospital stays. Patients can return to their daily activities much sooner compared to traditional open surgery, ensuring a quicker and smoother recovery.


 Lower Risk of Infection
Lower Risk of Infection
– Smaller wounds lower the risk of post-surgical infections. Minimally invasive surgery involves smaller incisions, reducing exposure to external contaminants. This significantly lowers the risk of post-surgical infections, promoting a safer and smoother healing process for patients.
 Less Scarring
Less Scarring
– Tiny incisions result in minimal scars compared to traditional open surgery. Minimally invasive surgery uses small incisions, resulting in minimal scarring. This not only enhances cosmetic outcomes but also reduces discomfort and promotes faster healing.

 Shorter Hospital Stay
Shorter Hospital Stay
– Many laparoscopic surgeries allow same-day discharge or shorter hospital stays. Minimally invasive surgery allows for quicker recovery, reducing the need for prolonged hospitalization. Patients can return home sooner, promoting comfort and faster healing in a familiar environment.
Common Surgeries Performed Laparoscopically
- Gallbladder Removal (Cholecystectomy)
- Hernia Repair
- Appendix Removal (Appendectomy)
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- Gynecological Procedures
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized the way surgeries are performed, offering patients a safer and quicker recovery option. If you are considering surgery and want to explore minimally invasive options, consult with an experienced laparoscopic surgeon to determine the best course of action for your condition.
💡 Need expert surgical care? Contact Dr. Nainesh Patel for advanced laparoscopic procedures and personalized treatment!


